Everything You Need to Know About Heart Disease
The most common cause of death in the US is heart disease . Many symptoms can be relieved by drugs, treatments, and lifestyle modifications, but the condition cannot be cured or reversed.
In the United States in 2021, heart disease claimed the lives of 1 in 5 people, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). That’s about 695,000 people.
What are the different types of heart disease?
Cardiovascular issues fall within the broad category of heart illness. Heart disease is a general term for a number of illnesses and disorders.
Heart disease comes in several forms:
Heart disorders that directly impact blood vessels can sometimes be referred to as "cardiovascular disease s."
What are the symptoms of heart disease?
Numerous heart disease s can result in a range of symptoms.
Arrhythmia
An irregular heart beat is called an arrhythmia. Depending on the kind of arrhythmia you have—such as an abnormally rapid or slow heart rate—your symptoms may vary.
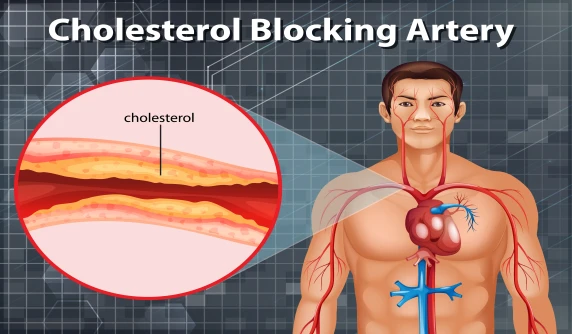
Atherosclerosis
Your extremities' blood flow is decreased by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis symptoms include weariness, weakness in the legs due to impaired circulation, and shortness of breath and chest pain.
Congenital heart defects
Heart issues known as congenital heart abnormalities arise during the growing fetus. Undiagnosed cardiac abnormalities can occur. When others exhibit symptoms, they might be identified.
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
Plaque accumulation in the arteries that provide oxygen-rich blood to the heart and lungs is known as CAD.
Cardiomyopathy
A condition called cardiomyopathy makes the heart muscles enlarge and become thick, inflexible, or weak.
Heart infections
Myocarditis and endocarditis are two illnesses that can result from heart infections.
What are the symptoms of heart disease in women?
In particular, women are more likely than men to exhibit distinct heart disease symptoms and indicators, such as CAD and other cardiovascular conditions.
The most common symptoms observed in women who had suffered a heart attack were examined in a 2016 study. The "classic" heart attack symptoms, such as tingling and chest discomfort, were not among the top symptoms. On the other hand, women were shown to be more prone to weariness, dyspepsia, and worry.
In women, heart disease symptoms can often be mistaken for symptoms of anxiety, menopause, and depression.
What causes heart disease?
Heart disease is an umbrella term for a number of illnesses and disorders that affect the circulatory system. The causes of each type of heart disease are completely specific to that illness.
Arrhythmia causes
A heart beat anomaly can be caused by the following:
-
Diabetes
-
Cad
-
Heart defects
-
High blood pressure (hypertension)
-
Certain medications
Congenital heart defect causes
This heart disease strikes during the fetus's development in the uterus. Certain heart problems can be dangerous and require prompt diagnosis and treatment. Some might also go years without receiving a diagnosis.
As you age, the composition of your heart may also alter. This may result in a cardiac defect, which could cause issues and difficulties.
Cardiomyopathy causes
Cardiomyopathy comes in various forms. Every kind is the outcome of a different circumstance:
-
Dilated cardiomyopathy (the most common type)
-
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
-
Restrictive cardiomyopathy
The reasons can be hereditary, comorbidities, or other medical disorders. Not all of the reasons are completely known.
Heart infection causes
Heart infections are most commonly caused by viruses, parasites, and bacteria. If left untreated, unchecked infections within the body can also cause damage to the heart.
What are some risk factors for heart disease?
Heart disease is associated with numerous risk factors. While some are under our control, others are not.
Approximately 47% of Americans, according to the CDC, have at least one heart disease risk factor. Among these risk factors are a few of them:
-
High blood pressure
-
Low levels of the "good" cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (hdl), and high cholesterol
-
Smoking
-
Obesity
-
Low physical activity
For instance, smoking is a modifiable risk factor. The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases states that smoking doubles a person's risk of heart disease.
Diabetes may potentially increase a person's risk of heart disease since elevated blood glucose levels raise the possibility of:
-
Angina
-
Heart attack
-
Stroke
-
Cad
Controlling your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes can reduce your risk of heart disease. Individuals who have diabetes and high blood pressure are more likely to develop cardiovascular disease.
Risk factors you can’t control
The following are other heart disease risk factors:
-
Family history
-
Ethnicity
-
Sex
-
Age
Even though you have no influence over these risk factors, you might be able to keep an eye on their impact.
It is especially concerning if there is a family history of CAD if it includes:
-
A male relative who is younger than 55.
-
A female relative who is younger than 65.
Those of Asian or Pacific Islander descent, non-Hispanic Black people, and non-Hispanic White individuals are more at risk than Native Americans or Alaskans.
In addition, men are more likely than women to get heart disease. Men are more likely than women to have heart disease, according to the CDC.
How is heart disease diagnosed?
In order to diagnose heart disease , your doctor may prescribe a variety of tests and examinations. You can get some of these tests done even before you start showing signs of heart disease .
When symptoms appear, more testing may be performed to explore for potential causes.
Physical exams and blood tests
A physical examination will be the first procedure your doctor does. Your medical history will be reviewed and your symptoms will be recorded.
They will next ask to see your personal and family medical history. In particular heart disease s, genetics may be a factor. Inform your physician if any close relatives suffer from heart disease .
Blood tests are routinely requested. This is because they can aid in the measurement of your cholesterol and the detection of inflammation indicators by your physician.
Noninvasive tests
Heart disease can be diagnosed using a range of noninvasive procedures, including:
-
Electrocardiogram (ekg)
-
Echocardiogram
-
Stress test
-
Carotid ultrasound
-
Holter monitor
-
Tilt-table test
-
Ct scan
-
Heart mri
Invasive tests
In order to identify the cause of your symptoms if a physical examination, blood tests, and noninvasive testing prove inconclusive, your doctor might wish to perform an internal examination. Among the invasive tests are:
-
Cardiac catheterization
-
Coronary angiography
-
Electrophysiology
What treatments are available for heart disease?
The kind of heart disease you have and its degree of progression will determine how your condition is treated. For instance, your doctor is probably going to prescribe an antibiotic if you have a heart disease .
If your doctor determines that you have plaque buildup, they may try to help you adopt specific lifestyle measures and prescribe a medicine that can help reduce your chance of developing new plaque buildup.
Heart disease treatment can be divided into three primary categories:
Lifestyle strategies
A few lifestyle choices can help keep your heart health y. Among them are:
-
Engaging in regular exercise.
-
Giving up smoking.
-
Restricting the amount of alcohol consumed.
Medications
Certain forms of heart disease may require the use of medicines. Medication prescribed by your doctor may help control or even reverse your heart disease .
Additionally, your doctor can recommend drugs that reduce or eliminate the chance of problems. Your specific prescription is based on the kind of heart disease you have. As examples, consider:
-
Beta-blockers
-
Blood thinners
-
Calcium channel blockers
-
Ace inhibitors
Surgery or invasive procedures
Surgery or other medical procedures may be required in certain heart disease cases in order to treat the illness and stop the symptoms from getting worse.
For instance, your doctor might place a stent in your artery to restore normal blood flow if plaque accumulation has totally or nearly completely clogged your arteries.
The type of heart disease you have and the degree of heart damage determine the technique your doctor will perform.
How can I prevent heart disease?
Certain heart disease risk factors, such as your family history, are uncontrollable. However, reducing the risk factors you can manage is still a crucial step in lowering your risk of heart disease .
Aim for normal cholesterol and blood pressure levels
Keeping your blood pressure and cholesterol within normal limits is one of the first things you can do to keep your heart health y. Blood pressure is measured using a unit called millimeters of mercury, often abbreviated as mm Hg.
Less than 120 systolic and 80 diastolic blood pressure, sometimes known as "120 over 80" or "120/80 mm Hg," is regarded as healthy.
Systolic pressure refers to the amount of pressure experienced during a heart beat. When the heart is at rest, the measurement is called diastolic. Greater values suggest that the heart is exerting too much effort to pump blood.
Your risk factors and your cardiac health history will determine your ideal cholesterol level. Your goal levels will be lower than those of those with low or average risk if you have diabetes, a high risk of heart disease, or if you have already experienced a heart attack.
Take up heart-healthy living practices
By adopting the same lifestyle practices that can assist you in managing heart disease , you can lower your risk of getting it.
For a total of two hours and thirty minutes each week, doctors advise exercising for thirty to sixty minutes most days. Consult your physician to ensure that you can safely follow these recommendations, particularly if you currently have a cardiac issue.
Because nicotine in cigarettes causes blood vessels to tighten, which makes it difficult for oxygenated blood to circulate, quitting smoking can improve your heart health . Atherosclerosis may result from this.
Furthermore, since long-term stress can hasten the onset of cardiac issues, controlling your stress can help reduce your risk of developing heart disease.
It may not be able to make all of these changes at once, and that's okay. Discuss with your physician what will matter most at this time. Making even little progress toward these objectives keeps you in optimal health .
Frequently asked questions
What is the relationship between high blood pressure and heart disease?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, increases the heart 's workload in order to pump blood. Narrowed arteries and thicker heart muscle may arise from this.
Additionally, the bigger and less elastic cardiac muscles caused by high blood pressure hinder the heart 's ability to pump blood. This lessens the flow of blood that is rich in oxygen, which is what your body needs.
Does heart disease have a treatment?
Heart disease requires lifetime care and monitoring because it cannot be cured or reversed. However, treatments, drugs, and lifestyle changes can reduce symptoms.
When all other treatments fail, bypass surgery or coronary intervention may be employed.
Does sinus bradycardia indicate a heart disease?
An unusually low heart rate is known as sinus bradycardia. On its own, it may not be a reason to worry. In fact, in young individuals or athletes, it's frequently a sign of a healthy heart. However, it can occasionally result in major heart issues.
Which activities are most beneficial for a heart valve leak?
Try your best to walk at a pace that allows you to breathe deeply and quickly while maintaining a conversational flow.
Using the same concept, you can perform various aerobic exercises like cycling or swimming.
Why are heart disease patients treated with beta-blockers?
Beta-blockers lessen the pace and force of your cardiac rhythm. They lower blood pressure as well. They function by preventing your body's beta receptors from being occupied by the hormone adrenaline, also known as epinephrine.
Conclusion
In the United States, about half of the population has an increased risk of heart disease , and the percentage is still rising.
Nonetheless, many occurrences of heart disease can be managed or prevented by implementing heart- health y lifestyle practices.
Although there are many advantages, these lifestyle adjustments are not always simple in our hectic and fast-paced lives. Your heart will be more likely to look after you in the future if you take care of it today.